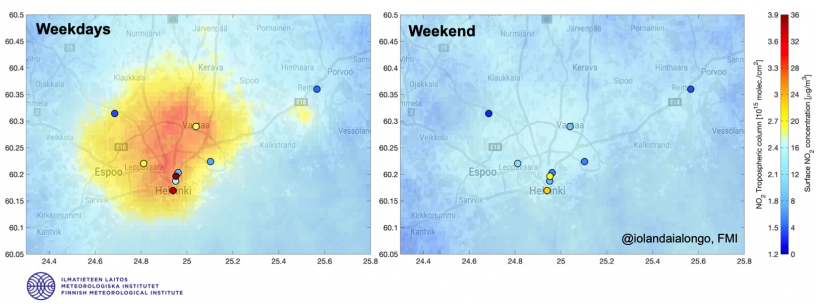
A new research led by researchers at the Space and Earth Observation Centre (FMI-SPACE) shows how satellite-based observations provide new accurate information for monitoring air pollution (in particular nitrogen dioxide, NO2) in the Helsinki region. The results show how commuter traffic strongly affects air quality in the capital region: NO2 concentrations are smaller during the weekend than during the working days. Also, the NO2 concentrations are smaller when the wind is stronger and the air pollutant gas dilutes faster. The largest NO2 concentrations correspond to the city center and the main traffic lanes as well as to the emission from oil refinery (Kilpilanti area in Porvoo) and power plants.
The results were obtained using tropospheric NO2 concentrations available since February 2018 from the TROPOMI (TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument) observations. TROPOMI is the only payload onboard the ESA’s Sentinel 5 Precursor satellite and it is part of the EU Copernicus Earth Observation program. TROPOMI observations showed similar spatio-temporal variability compared to ground-based measurements from Pandora spectrometer and air quality station in Kumpula, Helsinki.
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is a polluting gas produced from fossil fuel combustion processes, i.e. from transportation, energy production and industrial processes. NO2 is a short-lived gas and can be found in high concentrations close to the emission sources. TROPOMI retrievals are valuable to complement the ground-based air quality data and, due to their global coverage, can be used to monitor air pollution all over the world.
The research was carried out in collaboration with the Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) and was funded by the EU, ESA and Academy of Finland.
More information
Senior researcher Iolanda Ialongo, iolanda.ialongo@fmi.fi
Ialongo, I., Virta, H., Eskes, H., Hovila, J., and Douros, J.: Comparison of TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 Precursor NO2 observations with ground-based measurements in Helsinki, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 13, 205–218, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-13-205-2020, 2020.






Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.